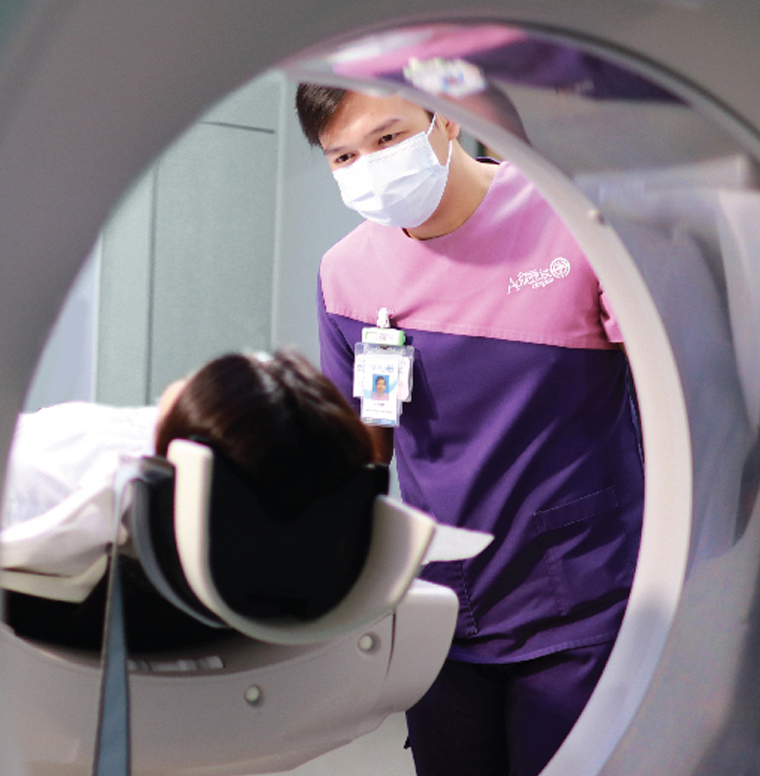

Mobile Digital X-ray is a bedside radiography examination which is on patients whom are unable to move from the bed to Diagnostic Imaging Department or any critically ill patient to avoid transports and extra movements.
Compared to conventional X-ray, it offers lesser processing time and eliminates long waiting times. Thus, Radiologists and patients can have accurate and high quality images in a short time, without risking patients to have to move to Diagnostic Imaging Department hence improve the overall patient care quality
On the other hand, children have different imaging needs as compared to adult patients. The Mobile Digital X-ray is able to offer dedicated low-dose organ programmes that allow imaging for the youngest patients quickly and easily.
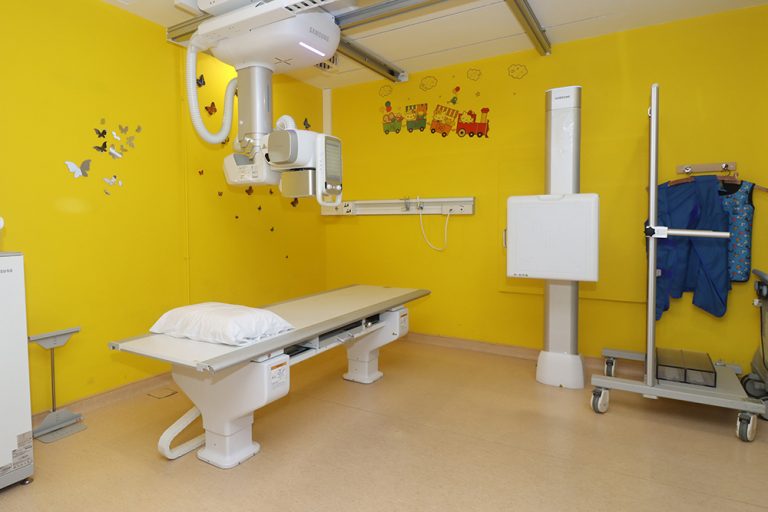
Digital radiography is a form of radiography that uses x-ray–sensitive plates to directly capture data during the patient examination, immediately transferring it to a computer system without the use of an intermediate cassette. Advantages include time efficiency through bypassing chemical processing and the ability to digitally transfer and enhance images. Also, less radiation can be used to produce an image of similar contrast to conventional radiography.
Instead of X-ray film, digital radiography uses a digital image capture device. This gives advantages of immediate image preview and availability; elimination of costly film processing steps; a wider dynamic range, which makes it more forgiving for over- and under-exposure; as well as the ability to apply special image processing techniques that enhance overall display quality of the image.
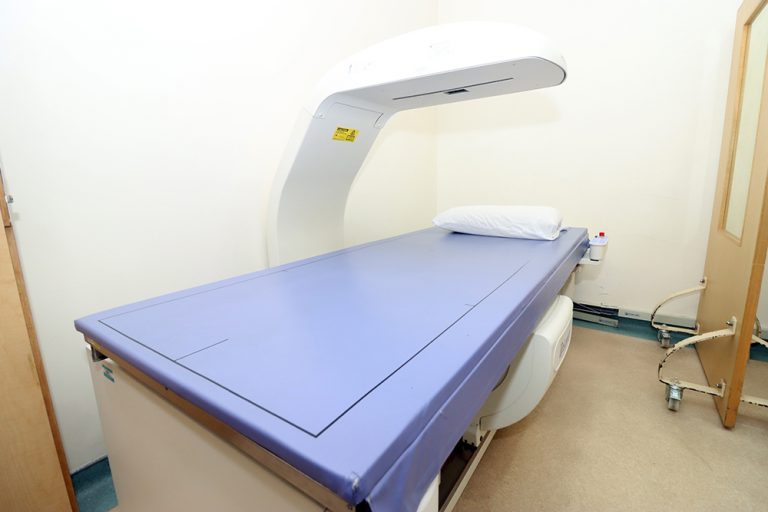
Bone densitometry is an X-ray procedure that measures bone loss due to osteoporosis, a disease that causes the loss of bone mass. Bone densitometry measurement is simple, safe, noninvasive, and painless.
After menopause, many women are at risk for osteoporosis. Early detection using bone density measurement is the best way to protect yourself from the potentially debilitating effects of osteoporosis. A bone density measurement will determine your bone mineral density (BMD) for the area measured.
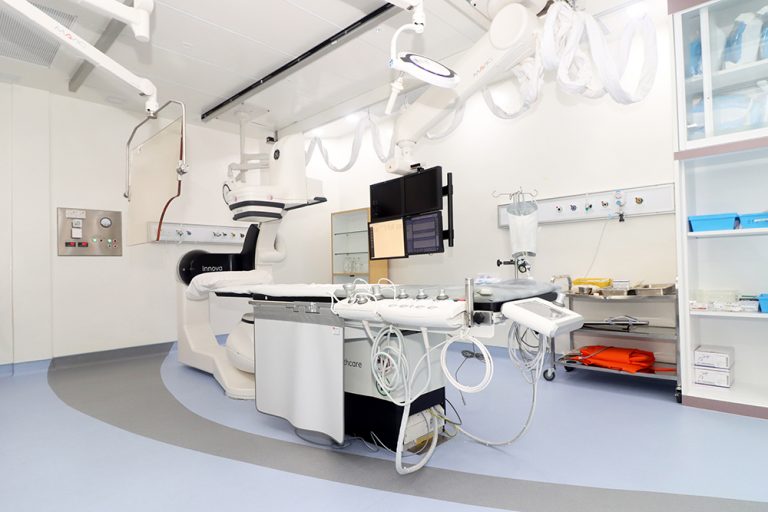
Cardiac catheterization (cardiac cath or heart cath) is a procedure to examine how well your heart is working. A thin, hollow tube called a catheter is inserted into a large blood vessel that leads to your heart. View an illustration of cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization is performed to find out if you have disease of the heart muscle, valves or coronary (heart) arteries. During the procedure, the pressure and blood flow in your heart can be measured. Coronary angiography (PDF) is done during cardiac catheterization. A contrast dye visible in X-rays is injected through the catheter. X-ray images show the dye as it flows through the heart arteries. This shows where arteries are blocked. The chances that problems will develop during cardiac cath are low.
“Interventional Radiology” (IR) refers to a range of techniques which rely on the use of radiological image guidance (X-ray fluoroscopy, ultrasound, computed tomography [CT] to precisely target the lesions. Most IR treatments are minimally invasive. As many IR procedures start with passing a needle through the skin to the target it is sometimes called pinhole surgery!
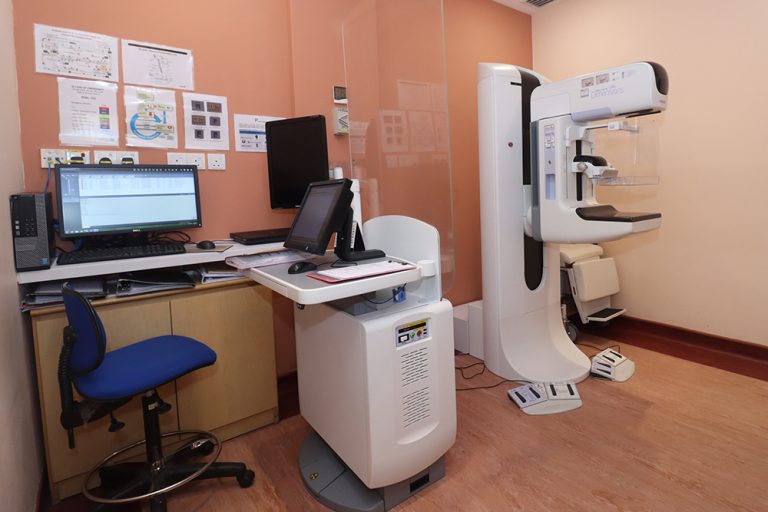
A 3D mammogram (breast tomosynthesis) is an imaging test that combines multiple breast X-rays to create a three-dimensional picture of the breast.
A 3D mammogram is used to look for breast cancer in people who have no signs or symptoms. It can also be used to investigate the cause of breast problems, such as a breast mass, pain and nipple discharge.
When used for breast cancer screening, 3D mammogram machines create 3D images and standard 2D mammogram images. Studies show that combining 3D mammograms with standard mammograms reduces the need for additional imaging and slightly increases the number of cancers detected during screening.
Screening mammography is the type of mammogram that checks you when you have no symptoms. It can help reduce the number of deaths from breast cancer among women ages 40 to 70. Mammograms are also recommended for younger women who have symptoms of breast cancer or who have a high risk of the disease.
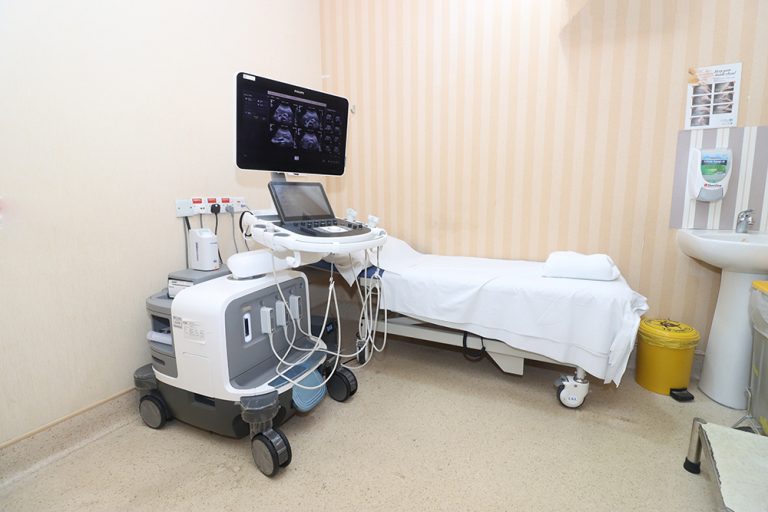
Diagnostic ultrasound, also called sonography or diagnostic medical sonography, is an imaging method that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of structures within your body. The images can provide valuable information for diagnosing and treating a variety of diseases and conditions. Most ultrasound examinations are done using an ultrasound device outside your body, though some involve placing a device inside your body.
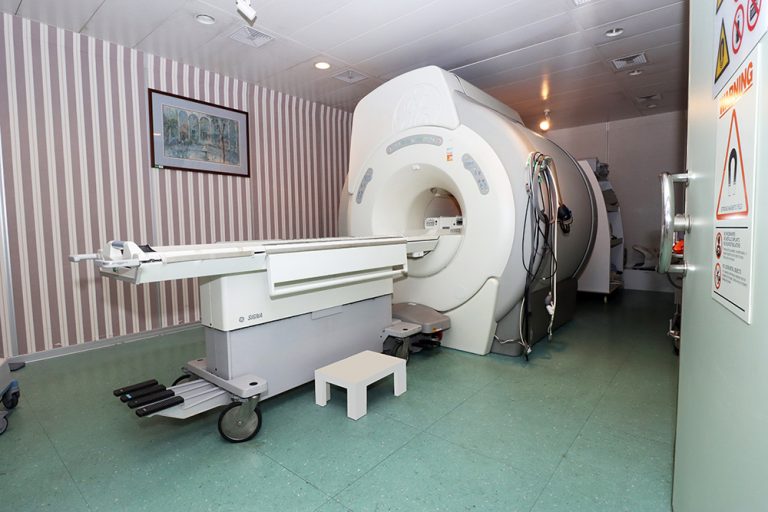
An MRI scan uses a large magnet, radio waves, and a computer to create a detailed, cross-sectional image of internal organs and structures. The scanner itself typically resembles a large tube with a table in the middle, allowing the patient to slide in. An MRI scan differs from CT scans and X-rays, as it does not use potentially harmful ionizing radiation.
Location | Adventist Diagnostic Imaging Department |
|---|---|
Monday – Thursday
| 8:00am – 5:00pm |
Friday & Sunday
| 8:00am – 1:00pm |
Saturday
| Closed |
Malaysia Website Design, Lightflex.